
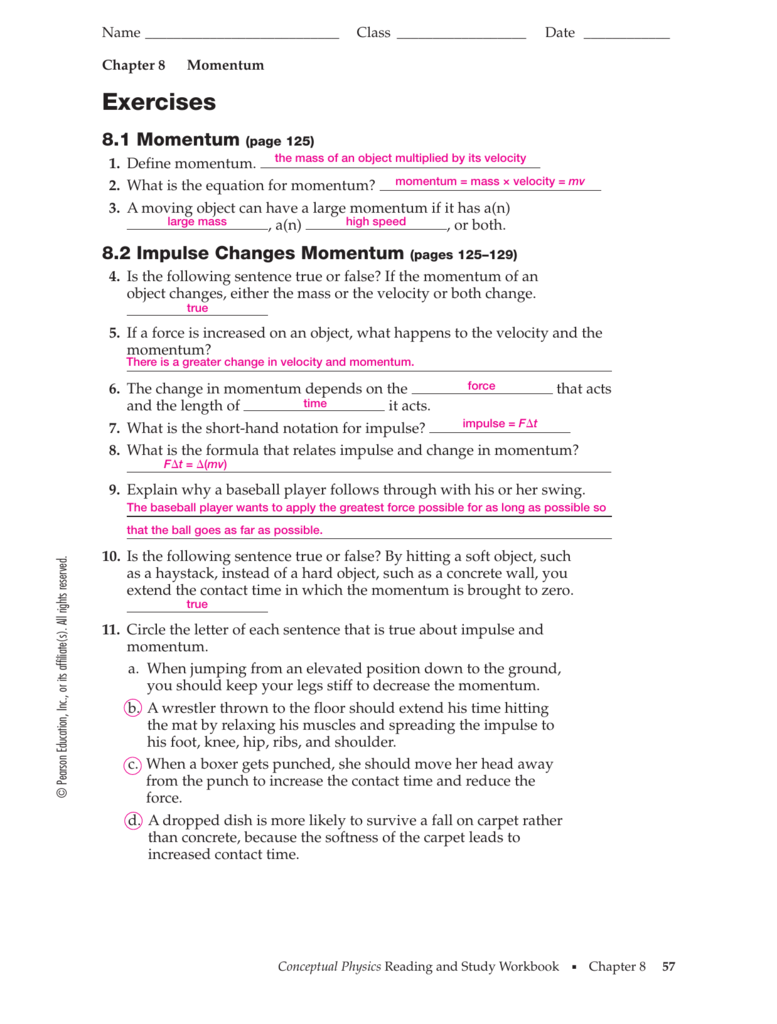
A 60 kg man standing on a stationary 40 kg boat throws a.Remember that momentum is a vector quantity.If the net external force is zero, then the total momentum of the system is constant.Assuming no mass enters or leaves the system, we define the total momentum of the system as the vector sum of the individual momentum of the particles: Suppose we have a system of N particles, with masses m1, m2,…, mn.Work done is a change in kinetic energy.Using the impulse-momentum theorem, calculate the time of flight of the ball. A ball of 2 kg is thrown straight up into the air with an initial velocity of 10 m/s.What was the change in momentum of the ball upon impact with the floor? What was the impulse provided by the floor? A 2 kg bouncy ball is dropped from a height of 10 meters, hits the floor and returns to its original height.If we take a time derivative of our momentum expression we get the following equation:.Relation between force and acceleration: A particle has linear momentum of 10 kg-m/s, and a kinetic energy of 25 J.From this definition we can generate two every important equations, the first relating force and acceleration, the second relating impulse and momentum. Again, momentum is a vector quantity, pointing in the direction of the velocity of the object.From our equation relating impulse and velocity, it is logical to define the momentum of a single particle, denoted by the vector p, as such: p= mv.What is the velocity of the ball after the force has acted on it? The ball has a mass of 2 kg and is initially at rest.What is the impulse of a force of 10 N acting on a ball for 2 seconds?.Can we predict the motion of an object? J = FΔt = (ma)Δt J = m Δt J = mΔv = Δ(mv) = mvf - mvo.Impulse can be defined mathematically, and is denoted by J: J= FΔt We shall define this concept, force applied over a time period, as impulse.How far from the shore does the raft move? The man walks toward the shore, the entire length of the raft. The edge of the raft is against the shore of the lake. A 50 kg man stands at the edge of a raft of mass 10 kg that is 10 meters long.
In what direction does the system travel? They are placed on a frictionless surface and separated so as to stretch the spring.

Calculate the center of mass of the following system: A mass of 5 kg lies at x = 1, a mass of 3 kg lies at x = 4 and a mass of 2 kg lies at x = 0.The concept of the center of mass allows us to describe the movement of a system of particles by the movement of a single point.We will now expand our study to systems of several particles.We have been studying the mechanics of single particles.Conservation of Momentum - The principle stating that for any system with no external forces acting on it, momentum will be conserved.Momentum - The product of an object's mass and velocity.Impulse - A force applied over a period of time.Center of Mass - The point at which a given net force acting on the system will produce the same acceleration as if all the mass were concentrated at that point.

8 Momentum and its conservation AP Physics C


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
